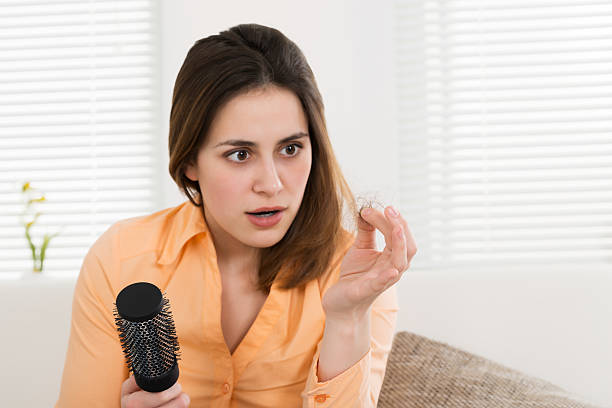
Whether you have been suffering from trichotillomania for a long time or have only recently noticed that it has begun to take a toll on your appearance, you will be glad to know that there are several different treatment options for this condition. These include herbal, physical, and psychological methods.
N-acetylcysteine
Several studies have suggested that N-acetylcysteine (NAC) can be an effective treatment for trichotillomania. This disorder involves the compulsive pulling of one’s own hair. A patient may experience a variety of symptoms, including difficulty concentrating, peer teasing, and medical complications. Trichotillomania usually has a chronic course, and can relapse.
N-acetylcysteine, or NAC, is a glutamate modulator. It normalizes glutaminergic transmission, which is implicated in the pathophysiology of trichotillomania. A study conducted by Dr. Jesus, of the Central Psychiatric Hospital of Lisbon, revealed that NAC significantly reduced hair pulling in trichotillomania patients.
The study was a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Half of the participants were given a daily dose of NAC, while the other half was given placebo. The study lasted for 12 weeks. The primary outcome of the study was the change in severity of hair pulling. A secondary outcome was comorbid anxiety.
Cognitive behavioral therapy
Among the treatments for trichotillomania, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is widely recognized as one of the most effective. A CBT therapist will work closely with the sufferer to assess the problem and develop a treatment plan.
CBT is a brief, action-oriented therapy that uses a number of techniques to help sufferers develop positive, non-pulling responses. It involves an assessment of symptoms and factors that contribute to trichotillomania, followed by short sessions in which the therapist works to change the behavior. The CBT sessions typically last less than an hour.
CBT sessions begin with an initial conversation between the patient and the therapist. The therapist will take notes on the patient’s current symptoms and factors that contribute to trichotillomania. During the first few sessions, the therapist will work with the patient to develop an action plan and teach the patient how to change his or her behavior.
Aromatherapy
Using aromatherapy as a treatment for trichotillomania is a great way to reduce the urge to pull hair. There are a number of different essential oils that can be used for this condition. These oils can be mixed together to create a blend that works better for you.
Lavender oil has been proven to relieve pain and anxiety. It has also been shown to help with depression.
Another essential oil that can be used to relieve stress is rosemary. This oil has anti-inflammatory properties and is also believed to help improve self esteem. It can also help with removing smells caused by sweat and clogged pores.
You can also use essential oils to treat fibromyalgia. These oils are inexpensive and easy to use. They can be applied during massages or diffused into the air.
Tricyclic antidepressants
Several pharmacologic treatments for trichotillomania have been studied, including antidepressants, glutamate-modulating agents, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. It is important to determine which treatment is best suited for each patient. There are also a number of nonpharmacologic treatments for trichotillomania, including psychotherapy, habit reversal training, and exposure and ritual prevention therapy.
Several studies have shown that tricyclic antidepressants can be effective in treating trichotillomania, though they are not for everyone. They are also known to have side effects, including blurred vision and weight gain.
Some patients who have used tricyclic antidepressants reported significant improvement, but other patients experienced adverse effects. In addition, tricyclic antidepressants can cause gastrointestinal complications, including decreased gut motility and constipation. A person should not drive while taking these drugs.
Tricyclics are also effective in treating depression, anxiety, and nocturnal enuresis. In some cases, tricyclic antidepressants have been effective in treating panic disorder.
Vitamin D deficiency
Several studies have shown that vitamin D deficiency is linked to a variety of psychiatric disorders. These include trichotillomania, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), hoarding disorder, body dysmorphic disorder, and excoriation disorder.
Vitamin D deficiency is usually treated with supplements or vitamin D rich foods. But in cases of severe deficiency, prescription vitamin D may be required. The Endocrine Society recommends 600 IU of vitamin D daily for adults and 400 IU daily for children.
Vitamin D is a fat soluble vitamin that is naturally found in the sun. It is converted in the liver into calcitriol, which binds to vitamin D receptors in almost every cell in the body.
Vitamin D deficiency is linked to bone loss, muscle weakness, osteomalacia, rickets, and cancer. It also plays a role in immune system function, inflammation, and the regulation of C-Ret, a gene that is important for cell differentiation.