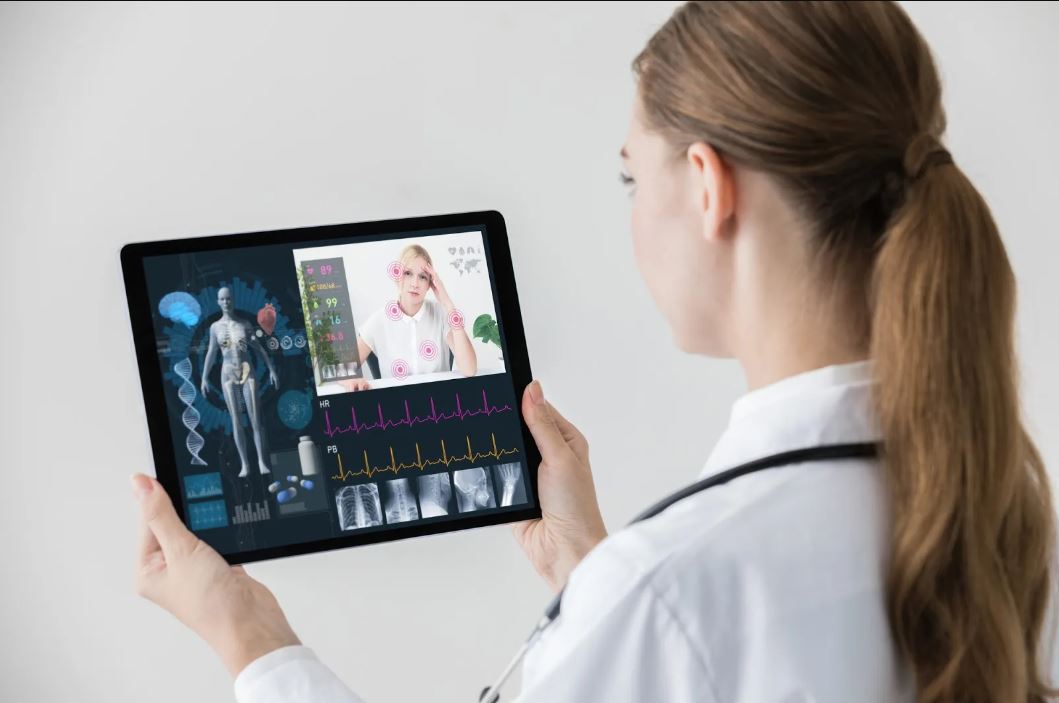
Telemedicine refers to the use of technology, such as video conferencing or telephone calls, to provide medical consultations and other healthcare services remotely. This allows patients to receive medical care without having to physically visit a healthcare facility.
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is a subcategory of telemedicine that involves the use of technology to collect and transmit health data from patients in one location to healthcare providers in another location. This can include monitoring vital signs, such as blood pressure and heart rate, as well as other health-related information, such as symptoms and medication use. The information is then used by healthcare providers to make treatment decisions and monitor the patient’s progress. RPM can be especially useful for patients with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or heart failure, who require frequent monitoring but may not be able to visit a healthcare facility as often as needed.
Read More: Sayed Quraishi
Types of Telemedicine Services
Telemedicine is the use of technology to provide medical consultations and other healthcare services remotely. It allows patients to receive medical care without having to physically visit a healthcare facility, making healthcare more accessible and convenient for many people. There are several different types of telemedicine services available, each with its own set of benefits and considerations.
- Virtual consultations: Virtual consultations, also known as e-visits or telehealth visits, involve real-time communication between a patient and a healthcare provider using video conferencing or telephone calls. Virtual consultations can be used for a wide range of healthcare services, such as diagnosing and treating illnesses, prescribing medications, and providing follow-up care. They are often used as a way to triage patients who do not need in-person visits, but still require medical attention.
- Remote monitoring: Remote monitoring, also known as remote patient monitoring (RPM), involves the use of technology to collect and transmit health data from patients in one location to healthcare providers in another location. This can include monitoring vital signs, such as blood pressure and heart rate, as well as other health-related information, such as symptoms and medication use. The information is then used by healthcare providers to make treatment decisions and monitor the patient’s progress. RPM can be especially useful for patients with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or heart failure, who require frequent monitoring but may not be able to visit a healthcare facility as often as needed.
- Store-and-forward: Store-and-forward telemedicine involves collecting and transmitting medical images, videos, or other data from a patient to a healthcare provider for review and diagnosis. This type of telemedicine is particularly useful for patients in remote or underserved areas, where access to specialists may be limited.
- Mobile health: Mobile health, or mHealth, refers to the use of mobile technology, such as smartphones or tablets, to provide healthcare services. This can include telemedicine services, such as virtual consultations and remote monitoring, as well as other health-related services, such as medication reminders and health education.
- Robotic telemedicine: Robotic telemedicine involves the use of robotic devices, such as telepresence robots, to provide medical consultations remotely. This type of telemedicine can be used to provide medical care in remote or underserved areas, where access to healthcare is limited.
In conclusion, the different types of telemedicine services offer a wide range of benefits, from increased access to healthcare for remote or underserved populations, to improved patient outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, telemedicine will likely become an increasingly i
Benefits of Telemedicine
Telemedicine is the use of technology to provide medical consultations and other healthcare services remotely. The technology allows patients to receive medical care without having to physically visit a healthcare facility. With the rise of telemedicine, patients can receive care in the comfort of their own homes, and healthcare providers can reach patients in remote or underserved areas. The benefits of telemedicine are numerous and include improved patient outcomes, increased access to healthcare, and cost savings.
- Increased access to healthcare: Telemedicine allows healthcare providers to reach patients in remote or underserved areas, where access to healthcare may be limited. This is especially important for patients living in rural areas, where access to specialists is often limited, and for patients with mobility issues. Telemedicine also allows patients to receive medical care without having to travel long distances, saving time and money.
- Improved patient outcomes: Telemedicine allows healthcare providers to monitor patients more closely, leading to better management of chronic conditions, such as diabetes or heart failure, and earlier detection of potential health problems. Additionally, telemedicine allows for more frequent check-ins with healthcare providers, which can lead to better management of symptoms and fewer hospital visits.
- Cost savings: Telemedicine can save patients money by reducing the need for in-person visits and travel to healthcare facilities. It can also save healthcare providers money by reducing the need for office visits and hospital stays. Additionally, telemedicine can be used to triage patients and reduce unnecessary in-person visits.
- Convenience: Telemedicine allows patients to receive medical care from the comfort of their own homes, without having to take time off work or arrange for transportation to a healthcare facility. Additionally, telemedicine allows for more flexible scheduling of appointments, making it easier for patients to see a healthcare provider when it is convenient for them.
- Improve patient engagement: Telemedicine can improve patient engagement, as it allows for more frequent communication between patients and healthcare providers. This can lead to better understanding of the patient’s condition and treatment, and can improve adherence to treatment plans, leading to better outcomes.
In conclusion, telemedicine offers a wide range of benefits, including increased access to healthcare, improved patient outcomes, cost savings, convenience and improved patient engagement. Telemedicine has the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery and make healthcare more accessible and convenient for patients and providers alike. As technology continues to evolve, telemedicine will likely play an increasingly important role in healthcare delivery.
Also, Read More: Understanding Anxiety in Adolescents
Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is a subcategory of telemedicine that involves the use of technology to collect and transmit health data from patients in one location to healthcare providers in another location. This can include monitoring vital signs, such as blood pressure and heart rate, as well as other health-related information, such as symptoms and medication use. The information is then used by healthcare providers to make treatment decisions and monitor the patient’s progress. RPM can be especially useful for patients with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or heart failure, who require frequent monitoring but may not be able to visit a healthcare facility as often as needed.
- Monitoring of chronic conditions: RPM is particularly useful for patients with chronic conditions, such as diabetes, heart failure, and COPD. These patients require frequent monitoring to manage their conditions and prevent complications. RPM allows healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely and make adjustments to treatment plans as needed, which can lead to better management of symptoms and fewer hospital visits.
- Early detection of potential health problems: RPM allows healthcare providers to monitor patients more closely, leading to earlier detection of potential health problems. This can lead to earlier intervention and treatment, which can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
- Cost savings: RPM can save patients and healthcare providers money by reducing the need for in-person visits and hospital stays. Additionally, RPM can be used to triage patients and reduce unnecessary in-person visits.
- Convenience: RPM allows patients to receive medical care from the comfort of their own homes, without having to take time off work or arrange for transportation to a healthcare facility. Additionally, RPM allows for more flexible scheduling of appointments, making it easier for patients to see a healthcare provider when it is convenient for them.
- Patient engagement: RPM can improve patient engagement, as it allows for more frequent communication between patients and healthcare providers. This can lead to better understanding of the patient’s condition and treatment, and can improve adherence to treatment plans, leading to better outcomes.
In conclusion, Remote patient monitoring is an innovative way of providing medical care to patients who need frequent monitoring. It allows healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely, detect potential health problems early, and make adjustments to treatment plans as needed. It also saves patients and healthcare providers money by reducing the need for in-person visits and hospital stays. Additionally, it is convenient for patients and improves patient engagement, leading to better outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, the use of RPM will likely become more widespread in the healthcare industry.
Telemedicine Equipment and Platforms
Telemedicine involves the use of technology to provide medical consultations and other healthcare services remotely. This technology includes a wide range of equipment and platforms, from video conferencing software to remote monitoring devices. These tools are essential for providing telemedicine services and are designed to make healthcare more accessible and convenient for patients and healthcare providers alike.
- Video conferencing software: Video conferencing software, such as Zoom, Skype, and Google Meet, is used for virtual consultations and remote visits. It allows healthcare providers to conduct real-time consultations with patients using video and audio. Video conferencing software can be used on a variety of devices, including computers, smartphones, and tablets.
- Remote monitoring devices: Remote monitoring devices, such as wearable devices and smart devices, are used to collect and transmit health data from patients to healthcare providers. These devices can include fitness trackers, smartwatches, and blood pressure monitors. They can be used to monitor vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels, as well as other health-related information, such as symptoms and medication use.
- Mobile health apps: Mobile health apps, or mHealth apps, are used to provide healthcare services using mobile technology. These apps can include telemedicine services, such as virtual consultations and remote monitoring, as well as other health-related services, such as medication reminders and health education.
- Electronic health records (EHR) systems: EHR systems are used to store and manage patient health information. They allow healthcare providers to access patient information, such as medical history, medications, and test results, remotely. This information can be used to inform treatment decisions and monitor patient progress.
- Telepresence robots: Telepresence robots are used in robotic telemedicine, they allow healthcare providers to remotely control a robotic device to interact with patients in remote or underserved areas. Telepresence robots can be used to conduct virtual consultations, take vital signs, and perform other medical procedures remotely.
In conclusion, telemedicine equipment and platforms are essential for providing telemedicine services. They include video conferencing software, remote monitoring devices, mobile health apps, EHR systems and telepresence robots. These tools are designed to make healthcare more accessible and convenient for patients and healthcare providers, and to improve patient outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, telemedicine equipment and platforms will likely become more sophisticated, making telemedicine an even more important component of healthcare delivery.
Telemedicine Regulations and Reimbursement
Telemedicine is the use of technology to provide medical consultations and other healthcare services remotely. While the benefits of telemedicine are numerous, there are also legal and financial considerations that must be taken into account. Regulations and reimbursement policies for telemedicine vary by state and by payer, making it important for healthcare providers and patients to understand the laws and regulations that apply to them.
- Laws and regulations: Telemedicine regulations vary by state and can include licensing requirements for healthcare providers, privacy and security regulations, and requirements for the use of telemedicine technology. For example, some states may require healthcare providers to have a separate license to practice telemedicine, while others may not. It is important for healthcare providers to understand the laws and regulations that apply to them in their state.
- Reimbursement policies: Reimbursement policies for telemedicine vary by payer and can include coverage for telemedicine services, reimbursement rates, and requirements for the use of telemedicine technology. For example, some payers may cover telemedicine services, while others may not. Additionally, reimbursement rates for telemedicine services may be lower than those for in-person services.
- Medicare and Medicaid: Medicare and Medicaid have specific policies and regulations regarding telemedicine. As of 2021, most Medicare beneficiaries are eligible for telemedicine services, but not all. Medicaid is also starting to cover telemedicine services, but policies vary by state.
- Private payers: Private payers also have their own policies and regulations regarding telemedicine. As of 2021, most private payers are covering telemedicine services, but not all. It is important to check with your insurance company to see what telemedicine services are covered and how much you will be reimbursed.
- HIPAA compliance: Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a federal law that requires healthcare providers to protect the privacy and security of patient health information. HIPAA compliance is mandatory for telemedicine services, and healthcare providers must implement appropriate safeguards to protect patient information.
In conclusion, while telemedicine offers a wide range of benefits, healthcare providers and patients must be aware of the legal and financial considerations associated with telemedicine. Regulations and reimbursement policies vary by state and payer, and it is important for healthcare providers and patients to understand the laws and regulations that apply to them. Additionally, compliance with HIPAA is mandatory for telemedicine services to ensure the protection of patient information. As telemedicine becomes more widely adopted, regulations and reimbursement policies are expected to evolve and become more favorable for telemedicine services.